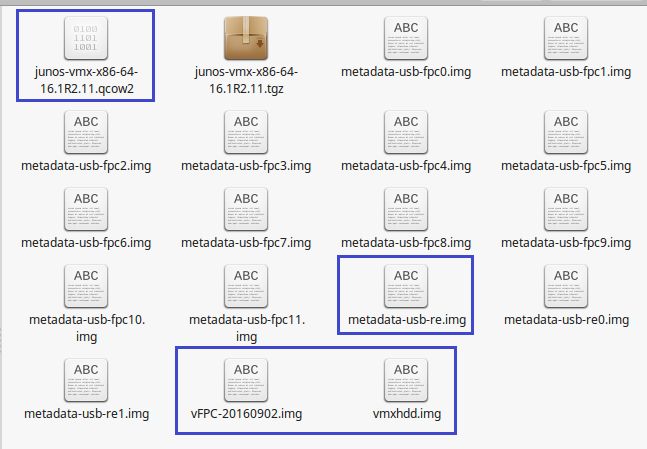
Is vMX 17.1R1.8 better/more stable than 17.2R1.13? (That's the version I have). Also, would you like the most recent version of vQFX? I've got it, as well. Just be aware that Juniper changes the filenames of the vFPC.img and the vmx.qcow2 file, with the different versions. They may even require we use a different metadata-usb-re.img in later releases. First, let’s create the vCP virtual machine, so we can run it via Qemu.
Juniper Vmx Qcow2 Download
These steps will help you install a Juniper vMX device on KVM. The steps assume you have already deployed a KVM host with all of the requirements that the vMX needs. If you did not already do this or you are deploying a new KVM host you can follow the instructions I have made here:
- — vmx.conf — vmx-junosdev.conf docs drivers — ixgbe-3.19.1 env images — jinstall64-vmx-15.1F4.15-domestic.img — jinstall64-vmx-15.1F4.15-domestic-signed.img — vmxhdd.img — vFPC20151203.img scripts — common — junosdev-bind — kvm — templates vmx.sh 29.
- Download Juniper vMX; Download Juniper vSRX and vSRX 3.0; Download Juniper vQFX; Download Juniper vRR; Download Junos Olive 12.1R1.qcow2 or.ova; Here is tutorial how to install vMX, vQFX, and vSRX on GNS3 and EVE-NG: Video How to Add Junos Olive on GNS3. Video How to Add Junos Olive on EVE-NG/a. Video How to Add and Setup Juniper vMX.
- CentOS 7.4 - I recommend using this as the Ubuntu support is patchy at best, the requirements for Ubuntu are also very old.
- Ubuntu 14.04I highly recommend that you deploy the host using the above instructions before continuing - deploying the vMX on a host that does not have the exact configuration required can be a frustrating experience.
For my vMX installations I am using SR-IOV for best performance, so the guide assumes that the interfaces assigned to the vFP are all SR-IOV. You will need to adjust the instructions depending on the vMX release that you are installing, I have extracted the vMX files to /home/vMX-[RELEASE] (in this case /home/vMX-18.1R1) so that when I upgrade the vMX I can keep the old copies in an obvious place.
Extract Files
- Download a copy of the vMX .tar.gz file for KVM on the host. Since I am deploying the vMX release 18.1R1, the file name is
vmx-bundle-18.1R1.9.tgz. The file can be downloaded from the Juniper vMX release page. This guide assumes that you have the .tar.gz file in/home/. - Extract the tar.gz file. The files will be extracted to
vmx/- I recommend renaming this to the release as well.
Intel X710/XL710 Drivers - Ubuntu Only
Note: These steps only apply to Ubuntu 14.04 hosts. Do not do this for a CentOS host. This step also assumes that you are using an Intel X710 or XL710 NIC.
There are two drivers that need to be installed - Intel i40evf and Intel i40e. The Intel i40evf driver needs to be downloaded from the Intel website, the i40e driver is included with the vMX. The i40e driver included with the vMX is patched to make certain features work when using SR-IOV, things like 802.3ad frames will not be passed through to the vMX otherwise.
- Try installing the i40e driver first included with the vMX:
If you are trying to install a different release of the vMX, the drivers folder will most likely be different (eg. for 17.4R1 the i40e driver is located in
drivers/i40e-1.3.46/srcinstead).
Make sure that this is successful. You may get errors when compiling the driver, as an example I got this error when deploying the vMX release 17.4R1:
If you do get errors like this, make sure that the kernel version that is currently running is supported by Juniper - check the 'Minimum Hardware and Software Requirements' page for the vMX release you are deploying to see which kernel is required. If you have the required kernel already installed but not running you will need to set Grub to use the older kernel and reboot the host to apply before continuing. Do not continue until this step works.
- Download a copy of the Intel i40evf driver from Intel and extract it:
- Install the i40evf driver:
- Update the init image so that the new driver is included:
- Activate the new driver (alternatively you can reboot the host):
Remove default bridge network - Ubuntu Only
Note: These steps only apply to Ubuntu 14.04 hosts. Do not do this for a CentOS host. This step also assumes that you are using an Intel X710 or XL710 NIC.
Remove the default bridge network that libvirt creates, this can cause issues starting the VM's for the vMX:
vMX Configuration File
The Juniper vMX configuration file needs to be created. The configuration file is in YAML format and defines what interfaces on the host to bind to the vMX and what resources the vMX will have. The Juniper vMX document from Juniper available here contains some sample configurations.
- Remove the default configuration file, its easier to copy the entire config from here and adjust as needed:
- Edit
vmx.confin your favourite editor. You will need to change a few values from the sample configuration file I have provided:- Update the
routing-engine-image,routing-engine-hddandforwarding-engine-imagepaths underHOST:to be the correct file locations - the RE engine image and vFPC image names may be different as well if you are using a release other than 18.1R1. - Set the appropriate
host-management-interface. This management interface is where the control plane and forwarding plane interfaces will be bound to to make the initial setup and troubleshooting more convenient. - Set the appropriate number of vCPU's for the control plane. For my case, 3 vCPU's is more than enough.
- Set the appropriate amount of RAM for the control plane. For my case 12GB is more than enough.
- Set the appropriate amount of vCPU's for the forwarding plane. There are specific requirements from Juniper for this (available here), make sure that you follow the requeirements for your use case. Since I am using performance mode with SR-IOV I have assigned 17 vCPU's.
- The number of vCPU's cannot be overcommitted. If you have a server with 24 logical CPU's (dual CPU, each CPU with 6 cores/12 threads for example) the maximum number of vCPU's you can allocate to both the control plane and forwarding plane cannot exceed 20 (4 CPU's must be left for the host).
- Set the correct IP details for the control plane and forwarding plane interfaces for management.
- The MAC adddresses in the configuration file can be any MAC addresses that you like - they must be unique though.
- Set the correct interfaces under
JUNOS_DEVICES:. These are the interfaces being assigned to the forwarding plane (revenue ports). All of the interfaces I am adding are 10G SR-IOV interfaces with the MTU set to 9400 (the maximum I can use). Thevirtual-functionshould not be changed unless you have specific requirements to do that.
- Update the
Here is the sample configuration you can use:
vMX Installation
The vMX can now be installed. The install process will also start the vCP and vFP VM's.
See Full List On Juniper.net
Run the installer with verbose logging just in case you run into issues:
Junos Vmx Qcow2 Download
The vMX should start up, once the vmx.sh script is finished running you can then access the console of the vCP and vFP. The default username for the routing engine is root with no password. After the vCP finishes booting (it could take a couple of minutes) you should also be able to reach the management IP that is configured. The management IP uses the fxp0 interface.
After the VM is booted, log in to the console you can do the minimal configuration to get SSH access:
- Set the root password:
set system root-authentication plain - Enable SSH with root login:
set system services ssh root-login allow - CommitYou can then SSH to the vCP management IP and continue the configuration. Using the console configuration will also work (the above 3 steps are not required) but there are issues if you are pasting in large amounts of configuration that are not present when using SSH. With release 18.1R1 I experienced an issue after doing the steps above where I lost reachability to the management IP (I couldn't ping or SSH to it anymore) - I had to stop and start the VM for that to work again.
I also recommend applying these settings:
- Apply the license to the VM. The default trial license will only allow 10mbit of throughput.
- Enable performance mode:
set chassis fpc 0 performance-mode - Set the number of ports for the FPC to the number of actual interfaces assigned to the vFP in the
vmx.conffile. Eg. if you have 6 interfaces assigned to the vFP:set chassis fpc 0 pic 0 number-of-ports 6 - Set the loopback device count to 1:
set chassis fpc 0 loopback-device-count 1
Starting on boot
To start the vMX on boot you will need to add either an init script (Ubuntu 14.04) or a systemd service (CentOS 7.4). I have included instructions on adding those and examples here.
Further Reading
I have some other guides available for enabling features as well as covering various errors that you may receive.
Hello there,
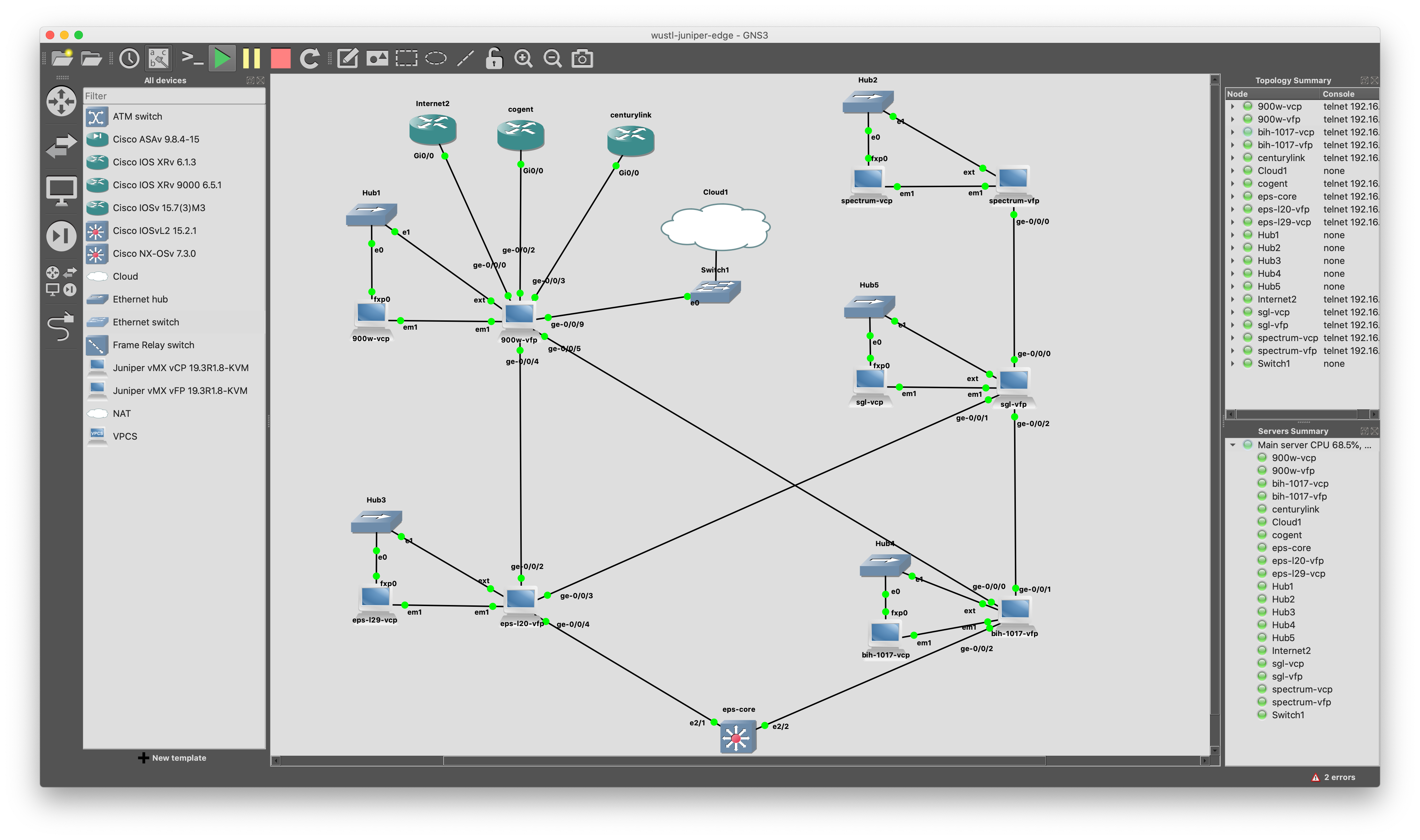
So, we are all aware of Juniper’s excellent series of routers and firewalls better known as MX Series Routers and SRX Security Devices or Firewalls. We all love doing labs, be it for our IT Certification or before deploying a major project. But buying expensive hardware is not always the best option. Introducing Juniper vMX & vSRX product portfolio not only helped the Service Providers and Enterprises deploy new services quickly but also it did help thousands of students and professionals globally to practice on real JunOS environment.Thus, in this short post I would love to show you how you can download Juniper vMX & vSRX and start your home lab in GNS3. Though this article mainly focuses on GNS3 environment, it can be deployed on ESXi also.
Time needed: 3 days.
Let’s look how to download Juniper vMX & vSRX (the official way)
- Visit Juniper’s Website
First of all visit https://www.juniper.net/us/en/dm/free-vmx-trial/ & https://www.juniper.net/us/en/dm/free-vsrx-trial/
They provide 60 days trials for the vMX and vSRX products, but limited to Juniper product owners only. - Create an Account in Juniper’s Website
A customer account is mandatory for downloading the trials. That means you must own a Juniper product or a Juniper Support Contract. Only then you might be provided access to these downloads. You need to key in the product serial or contract details for account creation. After request is submitted then it will be validated by Juniper Compliance team to get your account activated.
- Start the download
Once your account is activated, you may login and start to download Juniper vMX & vSRX trials from the links mentioned above.
- Download the license file
Once the download is completed, copy the license from the above links and save it in a notepad.
- Setup GNS3 Environment and start your lab
After all the files are in place, prepare your GNS3. I will write a separate blog post on How to setup Juniper vMX lab in GNS. Don’t forget to apply the license you have saved earlier for a flat 60 days eavluation.
See More Results
“The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot”
Michael AltshulerSo, let’s not waste time and see how to download latest Juniper vMX & vSRX in a super-fast way
- I have already made things easier for you. Just click on the below link and start your download.
Download Juniper vMX Evaluation –https://i.srijit.com/2wZce6x
Download Juniper vSRX Evaluation –https://i.srijit.com/2VSV56S - Once downloaded, prepare your GNS3 environment. As I said earlier, I will write a separate blog post on How to setup Juniper vMX lab in GNS. No need to worry!
- Start building your Juniper Lab.
Version and file details –
vMX –
👉 For ESXi environment – vmx-bundle-esxi-18.2R1.9.tgz
👉 For KVM environment (also for use with GNS3) – vmx-bundle-18.2R1.9.tgz
👉 Trial License for 60 days
vSRX –
👉 junos-vsrx3-x86-64-19.2R1.8.qcow2
👉 junos-vsrx3-x86-64-19.2R1.8.ide.ova
👉 junos-vsrx3-x86-64-20.1R1.11.qcow2
👉 junos-vsrx3-x86-64-20.1R1.11.ide.ova
👉 junos-media-vsrx-x86-64-vmdisk-20.1R1.11.qcow2
👉 junos-media-vsrx-x86-64-vmdisk-20.1R1.11.ide.ova
👉 Trial License for 60 days
Bonus Materials –
👉 GNS3 vCP and vFP appliance modified to support latest version vMX 18.2R1.9
👉 Juniper DayOne vMX Ebook
👉 Explore Junos CLI 2nd Edition Ebook
👉 JunOS for IOS Engineers Ebook
If your are looking for other versions of Juniper JunOS, I have a seperate blog for it here – http://srijit.com/download-working-juniper-junos-for-gns3/
Hope, it helped. All the best for your next lab and stay safe!
Video Tutorial